โมเดลแบบ Generative มีประสิทธิภาพในการแก้ปัญหาหลายประเภท อย่างไรก็ตาม โมเดลเหล่านี้มีข้อจำกัด เช่น
- โดยจะหยุดการอัปเดตหลังจากฝึกแล้ว ซึ่งทำให้ความรู้ล้าสมัย
- ผู้ใช้จะค้นหาหรือแก้ไขข้อมูลภายนอกไม่ได้
การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจะช่วยให้คุณเอาชนะข้อจำกัดบางอย่างเหล่านี้ได้ บางครั้งการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจะเรียกว่าการใช้เครื่องมือ เนื่องจากช่วยให้โมเดลใช้เครื่องมือภายนอก เช่น API และฟังก์ชัน เพื่อสร้างคำตอบสุดท้ายได้
คู่มือนี้จะแสดงวิธีตั้งค่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่คล้ายกับ สถานการณ์ที่อธิบายไว้ในส่วนหลักถัดไปของหน้านี้ ขั้นตอนการตั้งค่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันในแอปมีดังนี้
ขั้นตอนที่ 1: เขียนฟังก์ชันที่ให้ข้อมูลแก่โมเดลซึ่งโมเดลต้องใช้ในการสร้างคำตอบสุดท้าย (เช่น ฟังก์ชันสามารถเรียกใช้ API ภายนอกได้)
ขั้นตอนที่ 2: สร้างการประกาศฟังก์ชันที่อธิบายฟังก์ชันและพารามิเตอร์ของฟังก์ชัน
ขั้นตอนที่ 3: ระบุการประกาศฟังก์ชันในระหว่างการเริ่มต้นโมเดลเพื่อให้ โมเดลทราบวิธีใช้ฟังก์ชันหากจำเป็น
ขั้นตอนที่ 4: ตั้งค่าแอปเพื่อให้โมเดลส่งข้อมูลที่จำเป็น เพื่อให้แอปเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันได้
ขั้นตอนที่ 5: ส่งการตอบกลับของฟังก์ชันกลับไปยังโมเดลเพื่อให้โมเดล สร้างการตอบกลับสุดท้ายได้
ภาพรวมของตัวอย่างการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
เมื่อส่งคำขอไปยังโมเดล คุณยังระบุชุด "เครื่องมือ" (เช่น ฟังก์ชัน) ที่โมเดลใช้เพื่อสร้างคำตอบสุดท้ายได้ด้วย หากต้องการใช้ฟังก์ชันเหล่านี้และเรียกใช้ ("การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน") โมเดล และแอปของคุณต้องส่งข้อมูลไปมาถึงกัน ดังนั้น วิธีที่แนะนำในการใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันคือผ่านอินเทอร์เฟซแชทแบบหลายรอบ
สมมติว่าคุณมีแอปที่ผู้ใช้สามารถป้อนพรอมต์ เช่น
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?
Gemini โมเดลอาจไม่ทราบข้อมูลสภาพอากาศนี้ อย่างไรก็ตาม สมมติว่าคุณทราบ API บริการสภาพอากาศภายนอกที่ให้ข้อมูลนี้ได้ คุณสามารถใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเพื่อกำหนดเส้นทางให้โมเดล Gemini ไปยัง API และข้อมูลสภาพอากาศได้
ก่อนอื่นให้เขียนฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather ในแอปที่โต้ตอบกับ
API ภายนอกสมมติที่มีอินพุตและเอาต์พุตต่อไปนี้
| พารามิเตอร์ | ประเภท | ต้องระบุ | คำอธิบาย |
|---|---|---|---|
| อินพุต | |||
location |
ออบเจ็กต์ | ใช่ | ชื่อเมืองและรัฐที่จะรับข้อมูลสภาพอากาศ รองรับเฉพาะเมืองในสหรัฐอเมริกาเท่านั้น ต้องเป็นออบเจ็กต์ที่ซ้อนกันของ city และ state เสมอ
|
date |
สตริง | ใช่ | วันที่ที่จะดึงข้อมูลสภาพอากาศ (ต้องอยู่ในรูปแบบ YYYY-MM-DD เสมอ)
|
| เอาต์พุต | |||
temperature |
จำนวนเต็ม | ใช่ | อุณหภูมิ (หน่วยเป็นฟาเรนไฮต์) |
chancePrecipitation |
สตริง | ใช่ | โอกาสเกิดฝน/ลูกเห็บ/หิมะ (แสดงเป็นเปอร์เซ็นต์) |
cloudConditions |
สตริง | ใช่ | สภาพอากาศ (clear, partlyCloudy,
mostlyCloudy, cloudy)
|
เมื่อเริ่มต้นโมเดล คุณจะบอกโมเดลว่ามีfetchWeather
ฟังก์ชันนี้อยู่ และวิธีใช้ฟังก์ชันนี้เพื่อประมวลผลคำขอขาเข้าหากจำเป็น
ซึ่งเรียกว่า "การประกาศฟังก์ชัน" โมเดลไม่ได้เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
โดยตรง แต่ในขณะที่โมเดลประมวลผลคำขอที่เข้ามา โมเดลจะ
พิจารณาว่าfetchWeatherฟังก์ชันจะช่วยให้ตอบคำขอได้หรือไม่ หากโมเดลพิจารณาแล้วว่าฟังก์ชันนั้นมีประโยชน์จริง โมเดลจะสร้าง Structured Data ที่จะช่วยให้แอปของคุณเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
ดูคำขอที่เข้ามาอีกครั้ง
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? โมเดลน่าจะ
ตัดสินว่าฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather ช่วยสร้างคำตอบได้
โมเดลจะดูว่าต้องใช้พารามิเตอร์อินพุตใดสำหรับ fetchWeather จากนั้น
สร้างข้อมูลอินพุตที่มีโครงสร้างสำหรับฟังก์ชันที่มีลักษณะคล้ายกับตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
โมเดลจะส่งข้อมูลอินพุตที่มีโครงสร้างนี้ไปยังแอปเพื่อให้แอปเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather ได้ เมื่อแอปได้รับสภาพอากาศจาก API แล้ว แอปจะส่งต่อข้อมูลไปยังโมเดล ข้อมูลสภาพอากาศนี้ช่วยให้โมเดลประมวลผลขั้นสุดท้ายและสร้างคำตอบสำหรับคำขอเริ่มต้นของWhat was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?ได้
โมเดลอาจให้คำตอบสุดท้ายในภาษาธรรมชาติ เช่น
On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
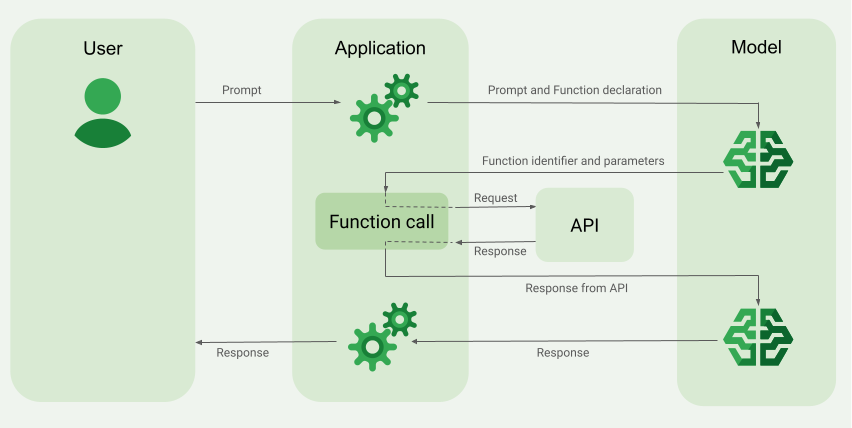
ใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน
ขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้ในคู่มือนี้จะแสดงวิธีติดตั้งใช้งานการเรียกฟังก์ชัน ที่คล้ายกับเวิร์กโฟลว์ที่อธิบายไว้ใน ภาพรวมของตัวอย่างการเรียกฟังก์ชัน (ดูส่วนบนของหน้านี้)
ก่อนเริ่มต้น
|
คลิกผู้ให้บริการ Gemini API เพื่อดูเนื้อหาและโค้ดของผู้ให้บริการรายนั้นๆ ในหน้านี้ |
หากยังไม่ได้ดำเนินการ ให้ทำตามคู่มือเริ่มต้นใช้งาน ซึ่งอธิบายวิธี
ตั้งค่าโปรเจ็กต์ Firebase, เชื่อมต่อแอปกับ Firebase, เพิ่ม SDK,
เริ่มต้นบริการแบ็กเอนด์สำหรับผู้ให้บริการ Gemini API ที่เลือก และ
สร้างอินสแตนซ์ GenerativeModel
สําหรับการทดสอบและทําซ้ำพรอมต์ เราขอแนะนําให้ใช้ Google AI Studio
ขั้นตอนที่ 1: เขียนฟังก์ชัน
สมมติว่าคุณมีแอปที่ผู้ใช้สามารถป้อนพรอมต์ เช่น
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? Gemini
โมเดลอาจไม่ทราบข้อมูลสภาพอากาศนี้ แต่สมมติว่าคุณทราบ
API บริการสภาพอากาศภายนอกที่ให้ข้อมูลนี้ได้ สถานการณ์ในคู่มือนี้
อิงตาม API ภายนอกสมมตินี้
เขียนฟังก์ชันในแอปที่จะโต้ตอบกับ API ภายนอกสมมติและให้ข้อมูลที่โมเดลต้องการเพื่อสร้างคำขอสุดท้าย ในตัวอย่างสภาพอากาศนี้ จะเป็นfetchWeatherฟังก์ชันที่
เรียกใช้ API ภายนอกสมมตินี้
Swift
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
Unity
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
ขั้นตอนที่ 2: สร้างการประกาศฟังก์ชัน
สร้างการประกาศฟังก์ชันที่คุณจะระบุในภายหลังให้กับโมเดล (ขั้นตอนถัดไปของคู่มือนี้)
ในการประกาศ ให้ใส่รายละเอียดให้มากที่สุดในคำอธิบายสำหรับ ฟังก์ชันและพารามิเตอร์ของฟังก์ชัน
โมเดลใช้ข้อมูลในการประกาศฟังก์ชันเพื่อพิจารณาว่าจะเลือกฟังก์ชันใดและจะระบุค่าพารามิเตอร์สำหรับการเรียกฟังก์ชันจริงอย่างไร ดูลักษณะการทำงานและตัวเลือกเพิ่มเติมในส่วนท้ายของหน้านี้เพื่อดูว่าโมเดลอาจเลือกฟังก์ชันต่างๆ อย่างไร รวมถึงวิธีควบคุมตัวเลือกนั้น
โปรดทราบข้อมูลต่อไปนี้เกี่ยวกับสคีมาที่คุณระบุ
คุณต้องระบุการประกาศฟังก์ชันในรูปแบบสคีมาที่เข้ากันได้ กับ สคีมา OpenAPI Vertex AI รองรับสคีมา OpenAPI แบบจำกัด
แอตทริบิวต์ที่รองรับ ได้แก่
type,nullable,required,format,description,properties,items,enumระบบไม่รองรับแอตทริบิวต์ต่อไปนี้
default,optional,maximum,oneOf
โดยค่าเริ่มต้น สำหรับ Firebase AI Logic SDK ระบบจะถือว่าช่องทั้งหมดเป็นต้องระบุ เว้นแต่คุณจะระบุเป็นไม่บังคับในอาร์เรย์
optionalPropertiesสำหรับฟิลด์ที่ไม่บังคับเหล่านี้ โมเดลสามารถป้อนข้อมูลในฟิลด์หรือข้าม ฟิลด์ได้ โปรดทราบว่าลักษณะการทำงานนี้จะตรงกันข้ามกับลักษณะการทำงานเริ่มต้นของ Gemini APIผู้ให้บริการทั้ง 2 รายหากคุณใช้ SDK ของเซิร์ฟเวอร์หรือ API ของผู้ให้บริการโดยตรง
ดูแนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำเกี่ยวกับการประกาศฟังก์ชัน รวมถึงเคล็ดลับสำหรับชื่อและคำอธิบายได้ที่ แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำ ในเอกสารประกอบของ Gemini Developer API
วิธีเขียนการประกาศฟังก์ชันมีดังนี้
Swift
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
Unity
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
ขั้นตอนที่ 3: ระบุการประกาศฟังก์ชันระหว่างการเริ่มต้นโมเดล
จำนวนประกาศฟังก์ชันสูงสุดที่คุณระบุได้ในคำขอคือ 128 รายการ ดูลักษณะการทำงานและตัวเลือกเพิ่มเติมในส่วนท้ายของหน้านี้เพื่อดูว่าโมเดลอาจเลือกฟังก์ชันใด รวมถึงวิธีควบคุมตัวเลือกนั้น (โดยใช้ toolConfig เพื่อตั้งค่าโหมดการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน)
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
ดูวิธีเลือกโมเดล ที่เหมาะสมกับกรณีการใช้งานและแอปของคุณ
ขั้นตอนที่ 4: เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเพื่อเรียกใช้ API ภายนอก
หากโมเดลตัดสินว่าฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather ช่วยให้โมเดลสร้างคำตอบสุดท้ายได้จริง
แอปของคุณจะต้องเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันนั้นจริง
โดยใช้ข้อมูลอินพุตที่มีโครงสร้างซึ่งโมเดลให้ไว้
เนื่องจากต้องมีการส่งข้อมูลไปมาระหว่างโมเดลกับแอป วิธีที่แนะนําในการใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันจึงทําผ่านอินเทอร์เฟซการแชทแบบหลายรอบ
ข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีที่แอปของคุณจะได้รับแจ้งว่าโมเดลต้องการใช้ฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather นอกจากนี้ ยังแสดงให้เห็นว่าโมเดลได้ระบุค่าพารามิเตอร์อินพุตที่จำเป็นสำหรับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน (และ API ภายนอกที่อยู่เบื้องหลัง)
ในตัวอย่างนี้ คำขอที่เข้ามามีพรอมต์
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? จากพรอมต์นี้ โมเดลได้อนุมานพารามิเตอร์อินพุตที่ฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather
ต้องการ (นั่นคือ city, state และ date)
Swift
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
Unity
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
ขั้นตอนที่ 5: ระบุเอาต์พุตของฟังก์ชันให้กับโมเดลเพื่อสร้างคำตอบสุดท้าย
หลังจากที่ฟังก์ชัน fetchWeather แสดงข้อมูลสภาพอากาศแล้ว แอปของคุณ
ต้องส่งข้อมูลดังกล่าวกลับไปยังโมเดล
จากนั้นโมเดลจะทำการประมวลผลขั้นสุดท้ายและสร้างคำตอบเป็นภาษาธรรมชาติขั้นสุดท้าย เช่น
On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Swift
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
Unity
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
ลักษณะการทำงานและตัวเลือกเพิ่มเติม
ลักษณะการทำงานเพิ่มเติมบางอย่างสำหรับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่คุณต้อง รองรับในโค้ดและตัวเลือกที่คุณควบคุมได้มีดังนี้
โมเดลอาจขอให้เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอีกครั้งหรือเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันอื่น
หากการตอบกลับจากการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหนึ่งไม่เพียงพอสำหรับโมเดลในการสร้าง การตอบกลับสุดท้าย โมเดลอาจขอการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเพิ่มเติม หรือ ขอการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันที่แตกต่างกันโดยสิ้นเชิง ซึ่งจะเกิดขึ้นได้ก็ต่อเมื่อคุณระบุฟังก์ชันมากกว่า 1 รายการให้กับโมเดลในรายการการประกาศฟังก์ชัน
แอปของคุณต้องรองรับกรณีที่โมเดลอาจขอฟังก์ชันเพิ่มเติม
โมเดลอาจขอเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายรายการพร้อมกัน
คุณระบุฟังก์ชันได้สูงสุด 128 รายการในรายการประกาศฟังก์ชันให้กับโมเดล ด้วยเหตุนี้ โมเดลจึงอาจตัดสินใจว่าต้องใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายอย่างเพื่อช่วยสร้างคำตอบสุดท้าย และอาจตัดสินใจเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันบางอย่างพร้อมกัน ซึ่งเรียกว่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบขนาน
แอปของคุณต้องรองรับกรณีที่โมเดลอาจขอให้เรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหลายอย่าง พร้อมกัน และแอปของคุณต้องส่งคำตอบทั้งหมดจาก ฟังก์ชันกลับไปยังโมเดล
คุณควบคุมได้ว่าโมเดลจะขอเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันหรือไม่และอย่างไร
คุณสามารถกำหนดข้อจำกัดบางอย่างเกี่ยวกับวิธีและเงื่อนไขที่โมเดลควรใช้ประกาศฟังก์ชันที่ระบุ ซึ่งเรียกว่าการตั้งค่าโหมดการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ตัวอย่างเช่น
คุณสามารถบังคับให้โมเดลใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันเสมอแทนที่จะอนุญาตให้โมเดลเลือกระหว่างการตอบกลับเป็นภาษาธรรมชาติทันทีกับการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ซึ่งเรียกว่าการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบบังคับ
หากคุณระบุการประกาศฟังก์ชันหลายรายการ คุณสามารถจำกัดโมเดลให้ใช้เฉพาะฟังก์ชันย่อยที่ระบุได้
คุณใช้ข้อจำกัด (หรือโหมด) เหล่านี้ได้โดยการเพิ่มการกำหนดค่าเครื่องมือ
(toolConfig) พร้อมกับพรอมต์และการประกาศฟังก์ชัน ในการกำหนดค่าเครื่องมือ คุณสามารถระบุโหมดใดโหมดหนึ่งต่อไปนี้ โหมดที่มีประโยชน์มากที่สุดคือ ANY
| โหมด | คำอธิบาย |
|---|---|
AUTO |
ลักษณะการทำงานเริ่มต้นของโมเดล โมเดลจะตัดสินใจว่าจะใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน หรือการตอบกลับด้วยภาษาธรรมชาติ |
ANY |
โมเดลต้องใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ("การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบบังคับ") หากต้องการจำกัด
โมเดลให้ใช้เฉพาะฟังก์ชันบางส่วน ให้ระบุชื่อฟังก์ชันที่อนุญาตใน
allowedFunctionNames
|
NONE |
โมเดลต้องไม่ใช้การเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชัน ลักษณะการทำงานนี้เทียบเท่ากับ คำขอโมเดลที่ไม่มีการประกาศฟังก์ชันที่เชื่อมโยง |
คุณทำอะไรได้อีกบ้าง
ลองใช้ความสามารถอื่นๆ
- สร้างการสนทนาแบบหลายรอบ (แชท)
- สร้างข้อความจากพรอมต์ข้อความเท่านั้น
- สร้างข้อความโดยการป้อนพรอมต์ด้วยไฟล์ประเภทต่างๆ เช่น รูปภาพ PDF วิดีโอ และ เสียง
ดูวิธีควบคุมการสร้างเนื้อหา
- ทำความเข้าใจการออกแบบพรอมต์ รวมถึง แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำ กลยุทธ์ และพรอมต์ตัวอย่าง
- กำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ของโมเดล เช่น อุณหภูมิและโทเค็นเอาต์พุตสูงสุด (สำหรับ Gemini) หรือสัดส่วนภาพ และการสร้างบุคคล (สำหรับ Imagen)
- ใช้การตั้งค่าความปลอดภัยเพื่อปรับ ความเป็นไปได้ที่จะได้รับคำตอบที่อาจถือว่าไม่เหมาะสม
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโมเดลที่รองรับ
ดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ โมเดลที่พร้อมใช้งานสำหรับกรณีการใช้งานต่างๆ รวมถึง โควต้าและ ราคาแสดงความคิดเห็น เกี่ยวกับประสบการณ์การใช้งาน Firebase AI Logic

