Üretken modeller, birçok türdeki sorunu çözme konusunda güçlüdür. Ancak bu işlevler aşağıdaki gibi sınırlamalarla kısıtlanmıştır:
- Eğitimden sonra donduruldukları için güncel olmayan bilgiler sunarlar.
- Harici verileri sorgulayamaz veya değiştiremezler.
İşlev çağrısı, bu sınırlamaların bazılarını aşmanıza yardımcı olabilir. İşlev çağrısı, bazen araç kullanımı olarak da adlandırılır. Bunun nedeni, bir modelin nihai yanıtını oluşturmak için API'ler ve işlevler gibi harici araçları kullanmasına olanak tanımasıdır.
Bu kılavuzda, bu sayfanın bir sonraki ana bölümünde açıklanan senaryoya benzer bir işlev çağrısı kurulumunu nasıl uygulayabileceğiniz gösterilmektedir. Genel olarak, uygulamanızda işlev çağrısını ayarlama adımları şunlardır:
1. adım: Modele nihai yanıtını oluşturmak için ihtiyaç duyduğu bilgileri sağlayabilecek bir işlev yazın (örneğin, işlev harici bir API'yi çağırabilir).
2. adım: İşlevi ve parametrelerini açıklayan bir işlev bildirimi oluşturun.
3. adım: Model başlatma sırasında işlev beyanını sağlayın. Böylece model, gerekirse işlevi nasıl kullanabileceğini bilir.
4. adım: Uygulamanızı, modelin işlevi çağırması için gereken bilgileri gönderebileceği şekilde ayarlayın.
5. adım: Modelin son yanıtını oluşturabilmesi için fonksiyonun yanıtını modele geri iletin.
İşlev çağırma örneğine genel bakış
Modele istek gönderdiğinizde, nihai yanıtını oluşturmak için kullanabileceği bir dizi "araç" (ör. işlevler) da sağlayabilirsiniz. Bu işlevleri kullanmak ve çağırmak ("işlev çağrısı") için modelin ve uygulamanızın birbirine bilgi iletmesi gerekir. Bu nedenle, işlev çağrısını kullanmanın önerilen yolu çok turlu sohbet arayüzüdür.
Kullanıcının aşağıdaki gibi bir istem girebileceği bir uygulamanız olduğunu düşünün:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?.
Gemini modelleri bu hava durumu bilgilerini bilmiyor olabilir. Ancak, bu bilgileri sağlayabilecek harici bir hava durumu hizmeti API'si olduğunu varsayalım. Gemini modeline bu API'ye ve hava durumu bilgilerine giden bir yol vermek için işlev çağrısını kullanabilirsiniz.
Öncelikle, uygulamanızda bu varsayımsal harici API ile etkileşim kuran bir işlev fetchWeather yazarsınız. Bu işlevin girişi ve çıkışı şöyledir:
| Parametre | Tür | Zorunlu | Açıklama |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giriş | |||
location |
Nesne | Evet | Hava durumunun alınacağı şehrin ve eyaletinin adı. Yalnızca ABD'deki şehirler desteklenir. Her zaman city ve state öğelerinin iç içe yerleştirilmiş bir nesnesi olmalıdır.
|
date |
Dize | Evet | Havanın alınacağı tarih (her zaman YYYY-MM-DD biçiminde olmalıdır).
|
| Çıkış | |||
temperature |
Tam sayı | Evet | Sıcaklık (Fahrenhayt cinsinden) |
chancePrecipitation |
Dize | Evet | Yağış ihtimali (yüzde olarak ifade edilir) |
cloudConditions |
Dize | Evet | Cloud koşulları (clear, partlyCloudy,
mostlyCloudy, cloudy)
|
Modeli başlatırken modele bu fetchWeather
işlevin var olduğunu ve gerekirse gelen istekleri işlemek için nasıl kullanılabileceğini söylersiniz.
Buna "işlev bildirimi" denir. Model, işlevi doğrudan çağırmıyor. Bunun yerine, model gelen isteği işlerken fetchWeather işlevinin isteğe yanıt vermesine yardımcı olup olamayacağına karar verir. Model, işlevin gerçekten yararlı olabileceğine karar verirse uygulamanızın işlevi çağırmasına yardımcı olacak yapılandırılmış veriler oluşturur.
Gelen isteğe tekrar bakın:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?. Model, fetchWeather işlevinin yanıt oluşturmasına yardımcı olabileceğine karar verebilir. Model, fetchWeather için hangi giriş parametrelerinin gerektiğini inceler ve ardından işlev için kabaca aşağıdaki gibi yapılandırılmış giriş verileri oluşturur:
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
Model, bu yapılandırılmış giriş verilerini uygulamanıza iletir. Böylece uygulamanız fetchWeather işlevini çağırabilir. Uygulamanız API'den hava durumu koşullarını aldığında bilgileri modele iletir. Bu hava durumu bilgisi, modelin son işlemeyi tamamlamasına ve What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? ilk isteğine yanıt oluşturmasına olanak tanır.
Model, aşağıdaki gibi nihai bir doğal dil yanıtı sağlayabilir:
On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
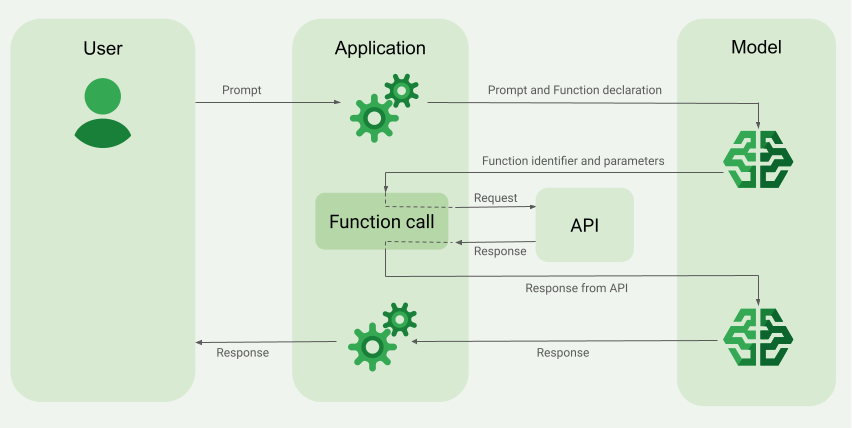
İşlev çağırmayı uygulama
Bu kılavuzdaki aşağıdaki adımlarda, İşlev çağrısı örneğine genel bakış bölümünde açıklanan iş akışına benzer bir işlev çağrısı kurulumunu nasıl uygulayacağınız gösterilmektedir (bu sayfanın üst kısmına bakın).
Başlamadan önce
|
Sağlayıcıya özel içerikleri ve kodu bu sayfada görüntülemek için Gemini API sağlayıcınızı tıklayın. |
Henüz yapmadıysanız başlangıç kılavuzunu tamamlayın. Bu kılavuzda Firebase projenizi ayarlama, uygulamanızı Firebase'e bağlama, SDK'yı ekleme, seçtiğiniz Gemini API sağlayıcısı için arka uç hizmetini başlatma ve GenerativeModel örneği oluşturma hakkında bilgiler yer almaktadır.
İstemlerinizi test etmek ve yinelemek için Google AI Studio kullanmanızı öneririz.
1. adım: Fonksiyonu yazın
Kullanıcının aşağıdaki gibi bir istem girebileceği bir uygulamanız olduğunu düşünün:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?. Gemini
Modeller bu hava durumu bilgilerini bilmiyor olabilir ancak bunu sağlayabilecek bir harici hava durumu hizmeti API'si bildiğinizi varsayalım. Bu kılavuzdaki senaryo, bu varsayımsal harici API'ye dayanmaktadır.
Uygulamanızda, varsayımsal harici API ile etkileşime girecek ve modele nihai isteğini oluşturması için gereken bilgileri sağlayacak işlevi yazın. Bu hava durumu örneğinde, bu varsayımsal harici API'ye çağrı yapan fetchWeather işlevi olacaktır.
Swift
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
Unity
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
2. adım: İşlev bildirimi oluşturun
Daha sonra modele sağlayacağınız işlev bildirimini oluşturun (bu kılavuzun sonraki adımı).
Beyanınızda, işlevin ve parametrelerinin açıklamalarına mümkün olduğunca fazla ayrıntı ekleyin.
Model, hangi işlevin seçileceğini ve işlevin gerçek çağrısı için parametre değerlerinin nasıl sağlanacağını belirlemek üzere işlev bildirimindeki bilgileri kullanır. Modelin işlevler arasında nasıl seçim yapabileceği ve bu seçimi nasıl kontrol edebileceğiniz hakkında bilgi edinmek için bu sayfanın ilerleyen bölümlerinde yer alan Ek davranışlar ve seçenekler'e bakın.
Sağladığınız şemayla ilgili olarak aşağıdakileri unutmayın:
İşlev bildirimlerini, OpenAPI şeması ile uyumlu bir şema biçiminde sağlamanız gerekir. Vertex AI, OpenAPI şeması için sınırlı destek sunar.
Şu özellikler desteklenir:
type,nullable,required,format,description,properties,items,enum.Şu özellikler desteklenmez:
default,optional,maximum,oneOf.
Varsayılan olarak, Firebase AI Logic SDK'larında tüm alanlar bir
optionalPropertiesdizisinde isteğe bağlı olarak belirtmediğiniz sürece zorunlu kabul edilir. Bu isteğe bağlı alanlar için model, alanları doldurabilir veya atlayabilir. Bu davranışın, iki sağlayıcının sunucu SDK'larını veya API'lerini doğrudan kullanırsanız varsayılan davranışın tam tersi olduğunu unutmayın. Gemini API
Adlar ve açıklamalarla ilgili ipuçları da dahil olmak üzere işlev bildirimleriyle ilgili en iyi uygulamalar için Gemini Developer API dokümanlarındaki en iyi uygulamalar Gemini Developer API
İşlev bildirimi şu şekilde yazılabilir:
Swift
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
Unity
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
3. adım: Model başlatma sırasında işlev beyanını sağlayın
İstekle birlikte sağlayabileceğiniz maksimum işlev bildirimi sayısı 128'dir. Modelin işlevler arasından nasıl seçim yapabileceği ve bu seçimi nasıl kontrol edebileceğiniz (toolConfig kullanarak işlev çağrısı modunu ayarlama) hakkında bilgi edinmek için bu sayfanın ilerleyen bölümlerinde Ek davranışlar ve seçenekler'e bakın.
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
Kullanım alanınıza ve uygulamanıza uygun bir model nasıl seçeceğinizi öğrenin.
4. adım: Harici API'yi çağırmak için işlevi çağırın
Model, fetchWeather işlevinin gerçekten nihai bir yanıt oluşturmasına yardımcı olabileceğine karar verirse uygulamanız, model tarafından sağlanan yapılandırılmış giriş verilerini kullanarak bu işlevi gerçekten çağırmalıdır.
Model ve uygulama arasında bilgi aktarılması gerektiğinden işlev çağrısını kullanmanın önerilen yolu çok turlu sohbet arayüzüdür.
Aşağıdaki kod snippet'inde, uygulamanıza modelin fetchWeather işlevini kullanmak istediğinin nasıl bildirildiği gösterilmektedir. Ayrıca, modelin işlev çağrısı (ve temelindeki harici API) için gerekli giriş parametresi değerlerini sağladığı da gösterilir.
Bu örnekte, gelen istek What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? istemini içeriyordu. Bu istemden yola çıkarak model, fetchWeather işlevi için gerekli olan giriş parametrelerini (yani city, state ve date) tahmin etti.
Swift
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
Unity
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
5. adım: Son yanıtı oluşturmak için işlevin çıkışını modele sağlayın
fetchWeather işlevi hava durumu bilgilerini döndürdükten sonra uygulamanızın bu bilgileri modele geri iletmesi gerekir.
Ardından model, son işlemini gerçekleştirir ve şu şekilde nihai bir doğal dil yanıtı oluşturur:
On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Swift
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
Unity
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
Ek davranışlar ve seçenekler
İşlev çağrısıyla ilgili olarak kodunuzda yer vermeniz gereken bazı ek davranışlar ve kontrol edebileceğiniz seçenekler aşağıda verilmiştir.
Model, bir işlevin veya başka bir işlevin tekrar çağrılmasını isteyebilir.
Bir işlev çağrısından gelen yanıt, modelin nihai yanıtını oluşturması için yeterli değilse model ek bir işlev çağrısı isteyebilir veya tamamen farklı bir işlevin çağrılmasını isteyebilir. Bu durum yalnızca işlev bildirimi listenizde modele birden fazla işlev sağlarsanız gerçekleşebilir.
Uygulamanız, modelin ek işlev çağrıları isteyebileceğini hesaba katmalıdır.
Model, aynı anda birden fazla işlevin çağrılmasını isteyebilir.
İşlev beyanı listenizde modele en fazla 128 işlev sağlayabilirsiniz. Bu nedenle model, nihai yanıtını oluşturmasına yardımcı olması için birden fazla işlevin gerekli olduğuna karar verebilir. Ayrıca bu işlevlerden bazılarını aynı anda çağırmaya karar verebilir. Bu işleme paralel işlev çağrısı denir.
Uygulamanız, modelin aynı anda birden fazla işlevin çalışmasını isteyebileceğini hesaba katmalı ve işlevlerden gelen tüm yanıtları modele geri göndermelidir.
Modelin işlevleri arama isteğinde bulunup bulunamayacağını ve bu isteğin nasıl yapılacağını kontrol edebilirsiniz.
Modelin, sağlanan işlev bildirimlerini nasıl ve kullanıp kullanmayacağı konusunda bazı kısıtlamalar uygulayabilirsiniz. Buna işlev çağrısı modu'nu ayarlama denir. Aşağıda bazı örnekler verilmiştir:
Modelin anında doğal dil yanıtı ve işlev çağrısı arasında seçim yapmasına izin vermek yerine, her zaman işlev çağrılarını kullanmaya zorlayabilirsiniz. Buna zorunlu işlev çağrısı denir.
Birden fazla işlev bildirimi sağlarsanız modeli yalnızca sağlanan işlevlerin bir alt kümesini kullanacak şekilde kısıtlayabilirsiniz.
Bu kısıtlamaları (veya modları), istem ve işlev bildirimleriyle birlikte bir araç yapılandırması
(toolConfig) ekleyerek uygularsınız. Araç yapılandırmasında aşağıdaki modlardan birini belirtebilirsiniz. En kullanışlı mod ANY.
| Mod | Açıklama |
|---|---|
AUTO |
Varsayılan model davranışı. Model, işlev çağrısı mı yoksa doğal dil yanıtı mı kullanacağına karar verir. |
ANY |
Model, işlev çağrılarını ("zorunlu işlev çağrısı") kullanmalıdır. Modeli işlevlerin bir alt kümesiyle sınırlamak için allowedFunctionNames içinde izin verilen işlev adlarını belirtin.
|
NONE |
Model, işlev çağrılarını kullanmamalıdır. Bu davranış, ilişkili işlev bildirimi olmayan bir model isteğine eşdeğerdir. |
Başka ne yapabilirsin?
Diğer özellikleri deneyin
- Çok adımlı görüşmeler (sohbet) oluşturun.
- Yalnızca metin içeren istemlerden metin oluşturun.
- Resim, PDF, video ve ses gibi çeşitli dosya türleriyle istem oluşturarak metin üretin.
İçerik oluşturmayı kontrol etme hakkında bilgi
- En iyi uygulamalar, stratejiler ve örnek istemler de dahil olmak üzere istem tasarımını anlama
- Sıcaklık ve maksimum çıkış parçası (Gemini için) ya da en boy oranı ve kişi oluşturma (Imagen için) gibi model parametrelerini yapılandırın.
- Zararlı olarak değerlendirilebilecek yanıtlar alma olasılığını ayarlamak için güvenlik ayarlarını kullanın.
Desteklenen modeller hakkında daha fazla bilgi
Çeşitli kullanım alanları için kullanılabilen modeller, bu modellerin kotaları ve fiyatlandırması hakkında bilgi edinin.Firebase AI Logic ile ilgili deneyiminiz hakkında geri bildirim verme
