Model generatif sangat andal dalam memecahkan berbagai jenis masalah. Namun, konfigurasinya dibatasi oleh batasan seperti:
- LLM dibekukan setelah pelatihan, sehingga pengetahuan yang ada dalamnya tidak diperbarui.
- LLM tidak dapat membuat kueri atau mengubah data eksternal.
Panggilan fungsi dapat membantu Anda mengatasi beberapa batasan ini. Panggilan fungsi terkadang disebut sebagai penggunaan alat karena memungkinkan model menggunakan alat eksternal seperti API dan fungsi untuk menghasilkan respons akhirnya.
Panduan ini menunjukkan cara mengimplementasikan penyiapan panggilan fungsi yang serupa dengan skenario yang dijelaskan di bagian utama berikutnya pada halaman ini. Secara umum, berikut adalah langkah-langkah untuk menyiapkan panggilan fungsi di aplikasi Anda:
Langkah 1: Tulis fungsi yang dapat memberikan informasi yang dibutuhkan model untuk membuat respons akhirnya (misalnya, fungsi dapat memanggil API eksternal).
Langkah 2: Buat deklarasi fungsi yang menjelaskan fungsi dan parameternya.
Langkah 3: Berikan deklarasi fungsi selama inisialisasi model sehingga model mengetahui cara menggunakan fungsi tersebut, jika diperlukan.
Langkah 4: Siapkan aplikasi Anda agar model dapat mengirimkan informasi yang diperlukan agar aplikasi Anda dapat memanggil fungsi.
Langkah 5: Teruskan respons fungsi kembali ke model agar model dapat membuat respons akhirnya.
Ringkasan contoh panggilan fungsi
Saat mengirim permintaan ke model, Anda juga dapat memberikan serangkaian "alat" (seperti fungsi) yang dapat digunakan model untuk membuat respons akhir. Untuk menggunakan fungsi ini dan memanggilnya ("panggilan fungsi"), model dan aplikasi Anda perlu mengirimkan informasi bolak-balik satu sama lain, sehingga cara yang direkomendasikan untuk menggunakan panggilan fungsi adalah melalui antarmuka chat multi-turn.
Misalnya, Anda memiliki aplikasi tempat pengguna dapat memasukkan perintah seperti:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?.
Model Gemini mungkin tidak mengetahui informasi cuaca ini; namun, bayangkan Anda mengetahui API layanan cuaca eksternal yang dapat menyediakannya. Anda dapat menggunakan panggilan fungsi untuk memberi model Gemini jalur ke API tersebut dan informasi cuacanya.
Pertama, Anda menulis fungsi fetchWeather di aplikasi yang berinteraksi dengan API eksternal hipotetis ini, yang memiliki input dan output berikut:
| Parameter | Jenis | Wajib | Deskripsi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | |||
location |
Objek | Ya | Nama kota dan negara bagiannya untuk mendapatkan cuaca. Hanya kota di Amerika Serikat yang didukung. Harus selalu berupa objek bertingkat dari city dan state.
|
date |
String | Ya | Tanggal untuk mengambil data cuaca (harus selalu dalam
format YYYY-MM-DD).
|
| Output | |||
temperature |
Bilangan bulat | Ya | Suhu (dalam Fahrenheit) |
chancePrecipitation |
String | Ya | Kemungkinan presipitasi (dinyatakan sebagai persentase) |
cloudConditions |
String | Ya | Kondisi awan (salah satu dari clear, partlyCloudy,
mostlyCloudy, cloudy)
|
Saat melakukan inisialisasi model, Anda memberi tahu model bahwa fungsi fetchWeather
ini ada dan cara menggunakannya untuk memproses permintaan yang masuk, jika diperlukan.
Hal ini disebut "deklarasi fungsi". Model tidak memanggil fungsi
secara langsung. Sebagai gantinya, saat model memproses permintaan yang masuk, model akan
memutuskan apakah fungsi fetchWeather dapat membantunya merespons permintaan tersebut. Jika
model memutuskan bahwa fungsi tersebut memang berguna, model akan membuat
data terstruktur yang akan membantu aplikasi Anda memanggil fungsi tersebut.
Lihat lagi permintaan yang masuk:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?. Model kemungkinan akan
memutuskan bahwa fungsi fetchWeather dapat membantunya menghasilkan respons. Model
akan melihat parameter input yang diperlukan untuk fetchWeather, lalu
membuat data input terstruktur untuk fungsi yang kurang lebih terlihat seperti ini:
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
Model meneruskan data input terstruktur ini ke aplikasi Anda sehingga aplikasi Anda dapat
memanggil fungsi fetchWeather. Saat aplikasi Anda menerima kembali kondisi cuaca dari API, aplikasi tersebut akan meneruskan informasi ke model. Informasi cuaca ini memungkinkan model menyelesaikan pemrosesan akhirnya dan menghasilkan respons terhadap permintaan awal What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?.
Model dapat memberikan respons akhir dalam bahasa alami seperti:
On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
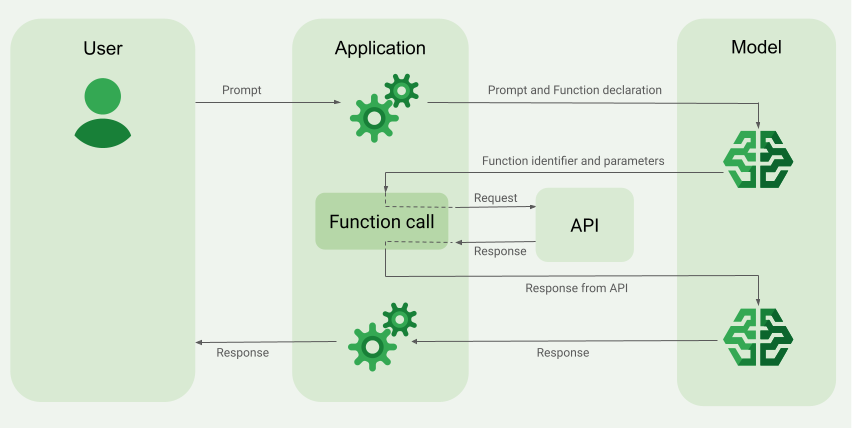
Menerapkan panggilan fungsi
Langkah-langkah berikut dalam panduan ini menunjukkan cara menerapkan penyiapan panggilan fungsi yang mirip dengan alur kerja yang dijelaskan dalam Ringkasan contoh panggilan fungsi (lihat bagian atas halaman ini).
Sebelum memulai
|
Klik penyedia Gemini API untuk melihat konten dan kode khusus penyedia di halaman ini. |
Jika belum melakukannya, selesaikan
panduan memulai, yang menjelaskan cara
menyiapkan project Firebase, menghubungkan aplikasi ke Firebase, menambahkan SDK,
menginisialisasi layanan backend untuk penyedia Gemini API yang Anda pilih, dan
membuat instance GenerativeModel.
Untuk menguji dan melakukan iterasi pada perintah Anda, sebaiknya gunakan Google AI Studio.
Langkah 1: Tulis fungsi
Misalnya, Anda memiliki aplikasi tempat pengguna dapat memasukkan perintah seperti:
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?. Model Gemini
mungkin tidak mengetahui informasi cuaca ini; namun, bayangkan Anda mengetahui
API layanan cuaca eksternal yang dapat menyediakannya. Skenario dalam panduan ini
mengandalkan API eksternal hipotetis ini.
Tulis fungsi di aplikasi Anda yang akan berinteraksi dengan API eksternal hipotetis dan memberikan informasi yang dibutuhkan model untuk membuat permintaan akhirnya. Dalam contoh cuaca ini, fungsi fetchWeather akan melakukan panggilan ke API eksternal hipotetis ini.
Swift
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
Unity
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
Langkah 2: Buat deklarasi fungsi
Buat deklarasi fungsi yang akan Anda berikan kepada model nanti (langkah berikutnya dalam panduan ini).
Dalam deklarasi Anda, sertakan detail sebanyak mungkin dalam deskripsi untuk fungsi dan parameternya.
Model menggunakan informasi dalam deklarasi fungsi untuk menentukan fungsi mana yang akan dipilih dan cara memberikan nilai parameter untuk panggilan aktual ke fungsi. Lihat Perilaku dan opsi tambahan di halaman ini untuk mengetahui cara model memilih di antara fungsi-fungsi tersebut, serta cara Anda mengontrol pilihan tersebut.
Perhatikan hal-hal berikut tentang skema yang Anda berikan:
Anda harus memberikan deklarasi fungsi dalam format skema yang kompatibel dengan skema OpenAPI. Vertex AI menawarkan dukungan terbatas untuk skema OpenAPI.
Atribut berikut didukung:
type,nullable,required,format,description,properties,items,enum.Atribut berikut tidak didukung:
default,optional,maximum,oneOf.
Secara default, untuk SDK Firebase AI Logic, semua kolom dianggap wajib diisi kecuali jika Anda menentukannya sebagai opsional dalam array
optionalProperties. Untuk kolom opsional ini, model dapat mengisi kolom atau melewatinya. Perhatikan bahwa hal ini berlawanan dengan perilaku default dari dua penyedia Gemini API jika Anda menggunakan SDK server atau API mereka secara langsung.
Untuk praktik terbaik terkait deklarasi fungsi, termasuk tips untuk nama dan deskripsi, lihat Praktik terbaik dalam dokumentasi Gemini Developer API.
Berikut cara menulis deklarasi fungsi:
Swift
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
Unity
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
Langkah 3: Berikan deklarasi fungsi selama inisialisasi model
Jumlah maksimum deklarasi fungsi yang dapat Anda berikan dengan
permintaan adalah 128. Lihat
Perilaku dan opsi tambahan
di bagian selanjutnya pada halaman ini untuk mengetahui cara model dapat memilih di antara fungsi, serta
cara Anda dapat mengontrol pilihan tersebut (menggunakan toolConfig untuk menyetel
mode panggilan fungsi).
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
Pelajari cara memilih model yang sesuai untuk kasus penggunaan dan aplikasi Anda.
Langkah 4: Panggil fungsi untuk memanggil API eksternal
Jika model memutuskan bahwa fungsi fetchWeather memang dapat membantunya membuat respons akhir, aplikasi Anda perlu melakukan panggilan aktual ke fungsi tersebut menggunakan data input terstruktur yang disediakan oleh model.
Karena informasi perlu dikirimkan bolak-balik antara model dan aplikasi, cara yang direkomendasikan untuk menggunakan panggilan fungsi adalah melalui antarmuka chat multi-turn.
Cuplikan kode berikut menunjukkan cara aplikasi Anda diberi tahu bahwa model ingin menggunakan fungsi fetchWeather. Hal ini juga menunjukkan bahwa model telah memberikan nilai parameter input yang diperlukan untuk panggilan fungsi (dan API eksternal yang mendasarinya).
Dalam contoh ini, permintaan yang masuk berisi perintah
What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?. Dari perintah ini, model menyimpulkan parameter input yang diperlukan oleh fungsi fetchWeather (yaitu, city, state, dan date).
Swift
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
Unity
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Langkah 5: Berikan output fungsi ke model untuk membuat respons akhir
Setelah fungsi fetchWeather menampilkan informasi cuaca, aplikasi Anda perlu meneruskannya kembali ke model.
Kemudian, model melakukan pemrosesan akhir, dan menghasilkan respons bahasa alami akhir seperti:
On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Swift
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
Unity
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
Perilaku dan opsi tambahan
Berikut beberapa perilaku tambahan untuk panggilan fungsi yang perlu Anda sesuaikan dalam kode dan opsi yang dapat Anda kontrol.
Model dapat meminta untuk memanggil fungsi lagi atau fungsi lain.
Jika respons dari satu panggilan fungsi tidak cukup bagi model untuk menghasilkan respons akhir, model dapat meminta panggilan fungsi tambahan, atau meminta panggilan ke fungsi yang sama sekali berbeda. Hal ini hanya dapat terjadi jika Anda memberikan lebih dari satu fungsi ke model dalam daftar deklarasi fungsi.
Aplikasi Anda harus mengakomodasi bahwa model dapat meminta panggilan fungsi tambahan.
Model dapat meminta untuk memanggil beberapa fungsi secara bersamaan.
Anda dapat menyediakan hingga 128 fungsi dalam daftar deklarasi fungsi ke model. Dengan demikian, model dapat memutuskan bahwa beberapa fungsi diperlukan untuk membantunya menghasilkan respons akhir. Selain itu, Compose dapat memutuskan untuk memanggil beberapa fungsi ini secara bersamaan – hal ini disebut panggilan fungsi paralel.
Aplikasi Anda harus mengakomodasi bahwa model dapat meminta beberapa fungsi yang berjalan secara bersamaan, dan aplikasi Anda harus memberikan semua respons dari fungsi kembali ke model.
Anda dapat mengontrol cara dan apakah model dapat meminta untuk memanggil fungsi.
Anda dapat menempatkan beberapa batasan tentang bagaimana dan apakah model harus menggunakan deklarasi fungsi yang diberikan. Tindakan ini disebut menyetel mode panggilan fungsi. Berikut beberapa contohnya:
Daripada mengizinkan model memilih antara respons bahasa alami langsung dan panggilan fungsi, Anda dapat memaksanya untuk selalu menggunakan panggilan fungsi. Hal ini disebut panggilan fungsi paksa.
Jika memberikan beberapa deklarasi fungsi, Anda dapat membatasi model agar hanya menggunakan subset fungsi yang diberikan.
Anda menerapkan batasan (atau mode) ini dengan menambahkan konfigurasi alat
(toolConfig) bersama dengan perintah dan deklarasi fungsi. Dalam konfigurasi alat, Anda dapat menentukan salah satu mode berikut. Mode yang paling berguna adalah ANY.
| Mode | Deskripsi |
|---|---|
AUTO |
Perilaku model default. Model memutuskan apakah akan menggunakan panggilan fungsi atau respons bahasa alami. |
ANY |
Model harus menggunakan panggilan fungsi ("panggilan fungsi paksa"). Untuk membatasi
model ke subset fungsi, tentukan nama fungsi yang diizinkan dalam
allowedFunctionNames.
|
NONE |
Model tidak boleh menggunakan panggilan fungsi. Perilaku ini setara dengan permintaan model tanpa deklarasi fungsi terkait. |
Kamu bisa apa lagi?
Mencoba kemampuan lain
- Bangun percakapan multi-turn (chat).
- Membuat teks dari perintah khusus teks.
- Buat teks dengan memberikan perintah menggunakan berbagai jenis file, seperti gambar, PDF, video, dan audio.
Mempelajari cara mengontrol pembuatan konten
- Pahami desain perintah, termasuk praktik terbaik, strategi, dan contoh perintah.
- Mengonfigurasi parameter model seperti suhu dan token output maksimum (untuk Gemini) atau rasio aspek dan pembuatan orang (untuk Imagen).
- Gunakan setelan keamanan untuk menyesuaikan kemungkinan mendapatkan respons yang dapat dianggap berbahaya.
Pelajari lebih lanjut model yang didukung
Pelajari model yang tersedia untuk berbagai kasus penggunaan dan kuota serta harganya.Memberikan masukan tentang pengalaman Anda menggunakan Firebase AI Logic

