Firebase App Hosting utilizes Cloud Build to transform your application source code into a containerized format suitable for deployment on Cloud Run.
The build process operates through the following key stages:
Ingest: Gathers your application source code and configuration.
Build: Installs dependencies and builds your application.
Handoff: Finalizes the production Cloud Run container.
These three steps correspond directly to build steps 1, 2 and 3 as displayed in Cloud Build in the Google Cloud Console:
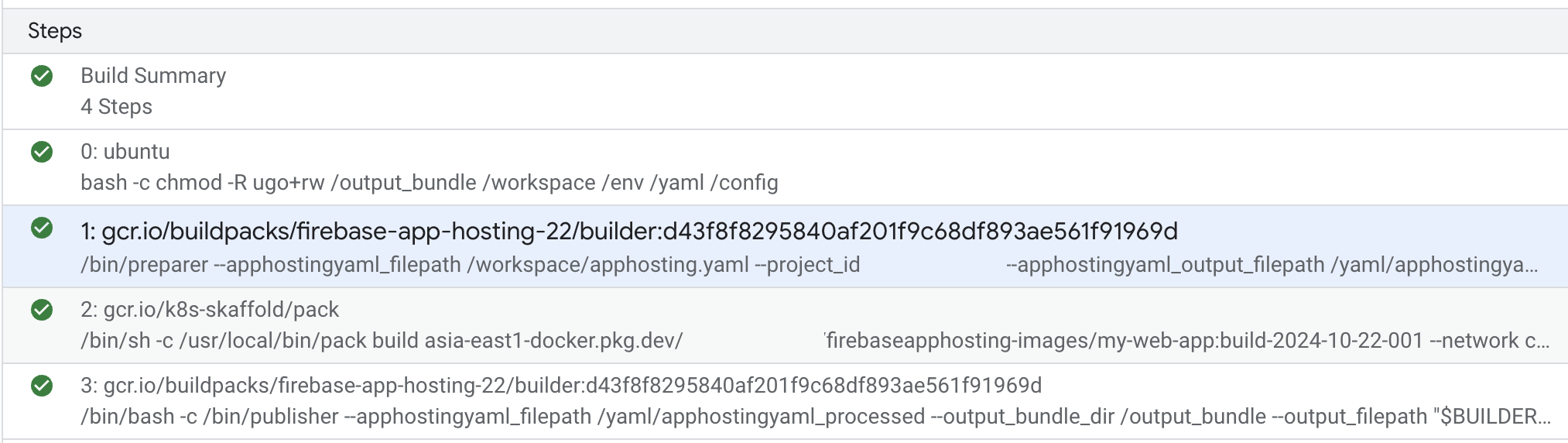
Ingest stage
This stage is responsible for handling pre-build logic. It reads, sanitizes, and
writes user-defined environment variables. It also dereferences and pins any
secrets specified in the apphosting.yaml file.
Build stage
This is the core of the build process, responsible for generating a runnable
container image and a bundle.yaml file defining your build configuration.
It utilizes Cloud Native Buildpacks
to package the
application efficiently. More information on the bundle.yamlfile can be found
on github.
Buildpacks are responsible for transforming your application source code into production ready container images. Firebase App Hosting chains together several buildpacks to complete the build process:
- Runtime Buildpack: Ensures all necessary components for running a basic Node.js application are included and dependencies are installed.
- Monorepo Buildpack: Configures subsequent buildpacks to handle different monorepo scenarios.
Framework Buildpack: Installs the correct framework adapter (like Angular or Next.js) and prepares subsequent buildpacks.
Framework adapters are in charge of running the productionized build command and mapping any relevant framework-specific config values to a standard format readable by App Hosting.
Package Manager Buildpack: Executes the installation of dependencies and builds the app using npm, yarn, or pnpm.
Output Bundle Buildpack: Defines the run command and prepares the output bundle for execution.
Handoff stage
This final stage packages all the information extracted from the application source code plus the build container image and sends it to the App Hosting backend. The App Hosting backend then uses this information to set up Cloud Run with the proper configurations.
Learn more
The entire App Hosting build process is open source.
- The buildpack code is in the Google Cloud buildpacks repo
- Code for framework adapters is in the firebase-framework-tools repo
- Learn more about Cloud Native buildpacks and Cloud Build
